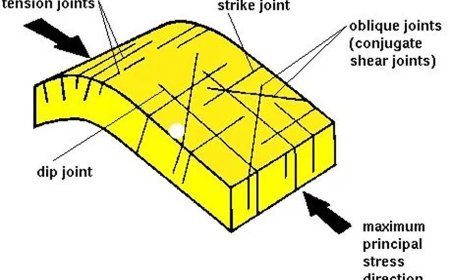
EARTH CAUSATIVE FACTORS
Explore the factors that shape our planet, from tectonic forces to human activities, and learn how they impact the Earth's systems.
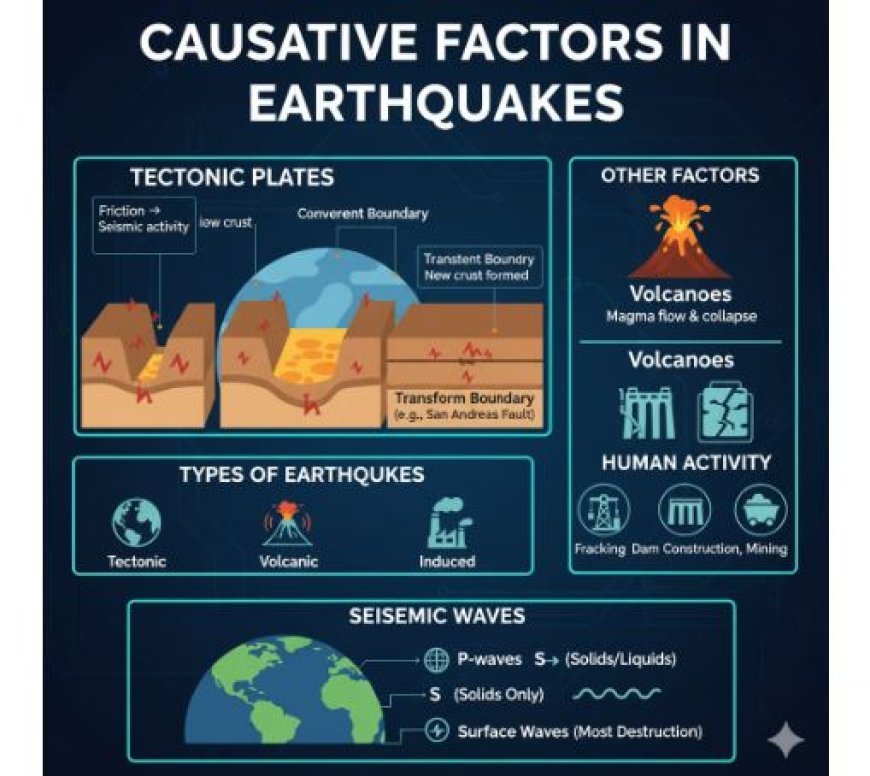
Causative Factors in Earthquakes
- Earthquakes, abrupt and often intense vibrations of the Earth's surface, are mainly induced by the dynamic motion of tectonic plates.
- Plate boundaries: The majority of earthquakes take place along the periphery of tectonic plates, where they interface with one another.
- At convergent boundaries, the collision of two plates typically results in one subducting under the other. Such phenomena may give rise to profound oceanic trenches and volcanic arcs.
- Friction between tectonic plates may result in seismic activity.
- Divergent boundaries result in the formation of fresh oceanic crust as plates separate. This phenomenon, often linked to volcanic eruptions, may also induce seismic events.
- Transform boundaries: The horizontal movement of plates past one another may result in substantial earthquakes. An example of this is the San Andreas Fault, located in California.
- Structural stress and strain accumulate along fault lines when plates undergo movement.
- When the tension surpasses the geological strength of the rocks, the fault breaks, liberating energy in the form of seismic waves.
Other Factors
- The flow of magma inside volcanoes has the potential to initiate earthquakes.
- Furthermore, seismic events may be triggered by the collapse of volcanic structures.
- Human Activity: Although less often, human activity may trigger earthquakes, including:
High-pressure injection of fluid into the subsurface, known as hydraulic fracturing (fracking), may increase seismic activity. - Dam Construction: The substantial mass of a dam may exacerbate the strain on the underlying faults.
- Excavating substantial quantities of material from the earth via mining may cause ground instability.
Types of earthquakes
- Tectonic earthquakes are the predominant kind of seismic activity resulting from the displacement of tectonic plates.
- Volcanic earthquakes pertain to seismic events that are linked to volcanic activity, resulting from either the flow of magma or the collapse of volcanic formations.
- Induced earthquakes are seismic events that are triggered by human actions. Although they are often smaller in size, they may still result in substantial destruction.
Seismic waves
- Body Waves: These waves propagate throughout the earthly interior.
- Primary waves, often known as P-waves, are compressional waves capable of propagating in both solid and liquid systems.
- Secondary waves, often known as S-waves, are shear waves that are limited to propagating through solid materials.
- The propagation of surface waves along the Earth's surface is the primary source of the majority of the destruction resulting from earthquakes.
What's Your Reaction?