DIAC
DIACs: Tiny Triggers, Big Impact - Bidirectional Switches for AC Control (Function + Application)
DIAC
- This word, diac, comes from the words DI and AC, which stand for "diode for alternating current."
- The device is a semiconductor switch that can work in both forward and backward bias regions. It's a thyrsistor and is used to turn on triacs and other devices that use thyrsistors.
- When the voltage goes over its break-over voltage, it starts to conduct. Also, it's like a transistor without a base.
- Both types of electricity can be turned "on" and "off." It comes in different kinds of packages.
- Small leaded packages, surface-mount packages, and big packages are all types of these packages.
- An electric device usually uses both a DIAC and a TRIAC together.
SYMBOL OF DIAC
- Two diodes are linked in the opposite direction to make a diac, which is a two-terminal device.
- Unlike other transistors that are used to start a circuit, like triacs, this one doesn't have a gate input.
- Because the DIAC is a two-way semiconductor device, we can't call those ends "anode" and "cathode."
- One of the DIAC terminals is called MT1 and the other is called MT2. MT stands for "main terminals."
The diac sign is shown below:
DIAC CONSTRUCTION
- The structure of the diac is like the structure of a transistor, but it doesn't have a base input.
- Each of the three layers has the same amount of doping, and the qualities of the material are the same in both directions of the applied voltage.
- Here are some of the main ways that a diac and a transistor are different:
- The amount of doping in the diac is the same in all layers, but in a transistor, the emitter is highly doped, the collector is lightly doped, and the base is fairly doped.
- A diode has two ends, while a transistor has three. All parts of a diamond are equal.
- It is made up of three, four, or five sets of semiconductors. The picture above shows the three-, four-, and five-layer building.
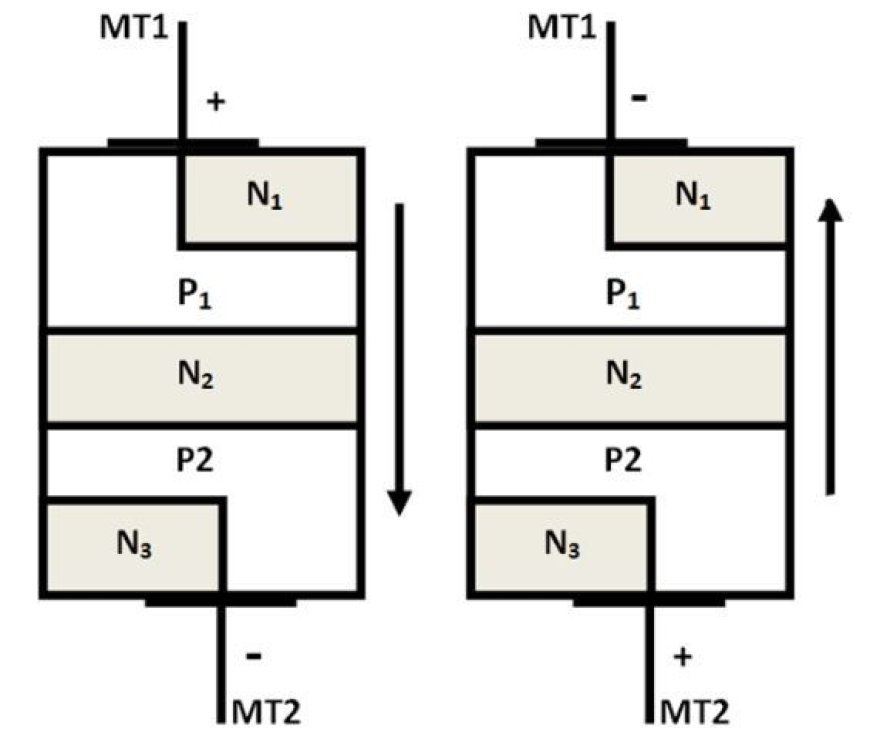
- Most of the time, three layers of PNP or NPN structure are used. The two main ends of PNP are MT1 and MT2, and they come from the outer P-region.
- The N-region is between them. We already know that it has two main ends, called MT1 and MT2, and that electricity can flow either way.
- As the power is put into the connections, these layers get turned on when the electricity hits them in the right way.
- When these two phases are mixed together, they make the DIAC conduct in both directions.
- The PNP structure is made up of three layers.
- Layers P1 and P2 link to MT1 and MT2, and the N-layer separates them. In a circuit where terminal 1 is positive compared to terminal 2, junctions P1 and N are forward biassed and junctions P2 and N are reverse biassed.
- The device switches to conduction mode when the voltage at the P2-N junction breaks through.
- That's why it's "ON" from terminal 1 to terminal 2. When terminal 2 is positive compared to terminal 1, the reverse bias arrives.
V-I CHARACTERISTICS OF DIAC
- Once it starts to conduct. It can work with electricity going either way. You can see the V-I feature curve of the diac in the picture above.
- The resistance will be high when the breakover voltage limit goes from -VBO to +VBO. So, a small amount of leakage current flows because the positive voltage is less than +VBO and the negative voltage is less than -VBO, as shown in the figure.
- As you can see from the picture, region AO is a blocked area. This is where the device acts as an open switch.
- The 30–50 volt breakover voltage band. The part "AB" shows how the gadget conducts electricity.
- Until the device's current drops below its holding current level, the device will keep working.
- It is worth mentioning that the holding and stopping currant values are the same in both the forward and backward regions.
- It shows the forward and revered features in the first and third quadrants, respectively.
Benefits of DIAC
- The device can be turned "ON" and "OFF" by lowering the voltage level below the point where it breaks.
- Using DIAC as a trigger circuit is a cheap way to do it.
Applications of DIAC
- If you connect the gate input to the DIAC, it can be used in the TRIAC activating circuit.
- It's used in a circuit for a dimmer lamp.
- In the main wire for the heater.
- It is in charge of controlling the universal motor's speed.
What's Your Reaction?


































