CHRONOSTRATIGRAPHY
Explore chronostratigraphy, the study of the time dimension of rock layers. Learn about its significance in reconstructing Earth's geological past and correlating rock formations.
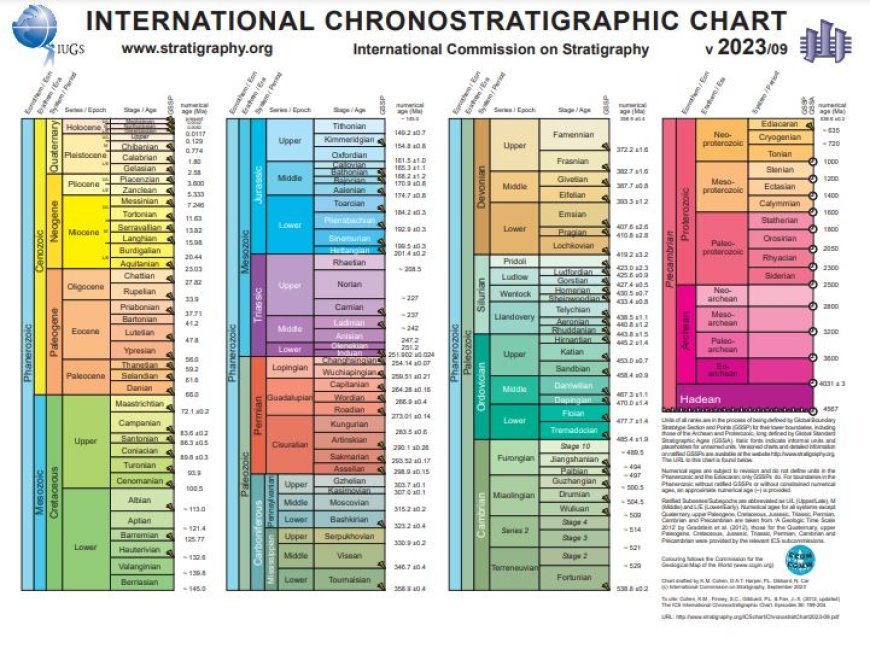
Chronostratigraphy
- Chronostratigraphy is the field of geology that analyzes the age of rock strata across time.
- The major objective is to link rocks that formed simultaneously in order to recreate historical events and depositional conditions in Earth's history. This is critical for understanding geological history and discovering resources such as oil.
Techniques for Chronostratigraphy
- Event stratigraphy identifies the sedimentary impact of extraordinary occurrences over different stratigraphic columns.
- Examples include volcanic ash layers, impact debris layers, and tsunami deposits.
- Usefulness: It helps link sections by establishing that sedimentary impacts occurred concurrently in distinct areas.
- Magnetostratigraphy is a method of dating rock strata based on their magnetic characteristics.
Measures the magnetic polarity of rock strata, which may be compared to known geomagnetic reversal patterns. - Biostratigraphy is the use of fossil material to correlate and date rock layers, making it useful for dating sedimentary and volcanic sequences.
- Process: identifies and matches fossil assemblages in various sites.
- Chemostratigraphy is a technique that correlates and dates rock strata based on their chemical composition, making it especially effective in marine deposits with numerous fossils.
- The process involves analyzing changes in chemical elements, or isotopes, within the layers.
- Sequence stratigraphy is the study of rock layers to understand the depositional environment and changes over time. It is useful for linking sedimentary sequences when other approaches are ineffective.
- Process: Examines sedimentary sequences and their boundaries.
- Chronostratigraphy is a commonly used method in petroleum geology to detect prospective hydrocarbon reserves.
- Reconstructing geological history helps to comprehend the succession of geological events and the evolution of the Earth's surface.
- Resource Exploration: Identifies rock units of comparable age, which aids in the discovery of lucrative resources such as oil and gas.
- Environmental Studies: Provides information on previous climatic changes and environmental circumstances.
What's Your Reaction?