THE POSSESSIVE CASE
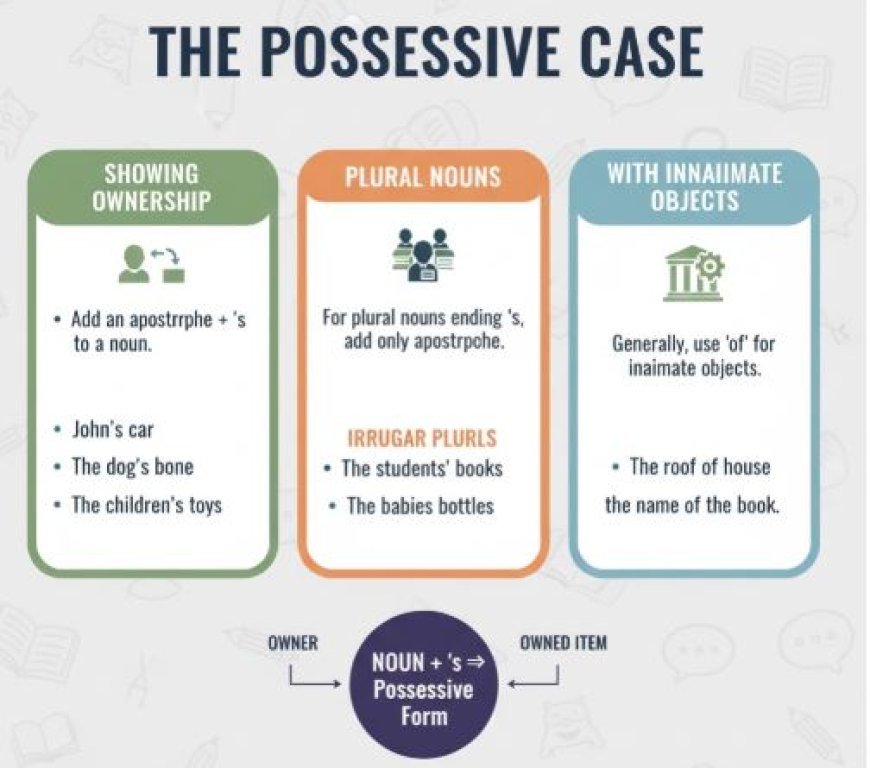
Possessive case shows ownership (whose what) with an apostrophe 's or just an apostrophe
THE POSSESSIVE CASE
- In the realm of English grammar, the possessive case plays a vital role in indicating ownership or belonging. Imagine it as a special detective discovering who or what something belongs to. Let's delve into this crucial concept without any plagiarism!
- Simply put, the possessive case indicates who or what owns something. We utilize various techniques to achieve this, not just the apostrophe you might be familiar with.
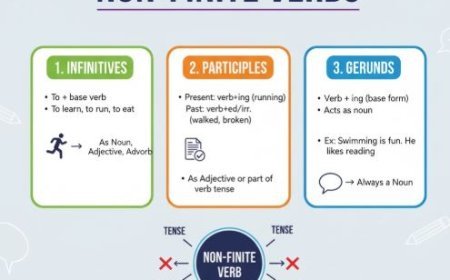
Types of Possessive Cases
- Possessive Nouns
- Formed by adding an apostrophe and "s" to singular nouns and irregular plural nouns (e.g., the doctor's appointment, children's laughter).
- For plural nouns ending in "s," just add an apostrophe (e.g., the teachers' lounge).
- Example:The dog's tail wagged excitedly. (The tail belongs to the dog.)
- Possessive Pronouns
- Words like "mine," "hers," "theirs," etc. directly indicate ownership without needing a noun (e.g., This book is mine). Is that yours?
- Example:She lost her phone, but thankfully her friend found it.
- Gerunds as Possessives
- Use gerunds (verbs ending in "-ing") to show ownership (e.g., the building's construction, walking the dog's leash).
- Example:Swimming is my favorite exercise. (The action of swimming belongs to me.)
What's Your Reaction?