METAL-OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR (MOSFET)
The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is a tiny, voltage-controlled switch used in electronics for amplification or switching signals.
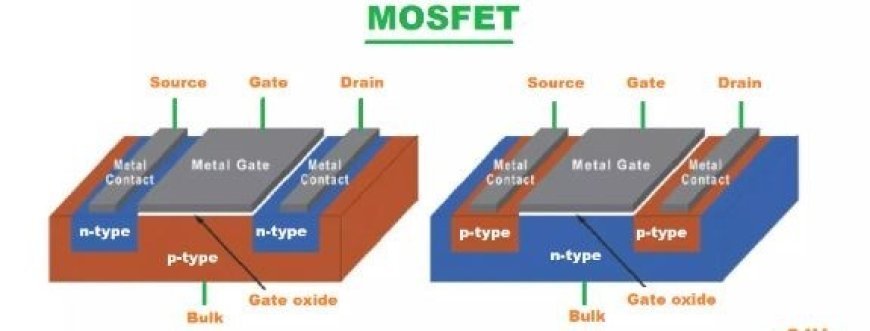
Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
- The MOSFET is another kind of field-effect transistor (FET) that can change the direction of electrical data or make them stronger.
- There is a shielded gate inside that controls how well the gadget conducts electricity based on the voltage that is applied.
- Because of this, it can be used to switch electrical signals or boost them by changing how well it conducts electricity when the voltage level changes.
- The main benefit of MOSFETs over bipolar transistors (BJTs or bipolar junction transistors) is that they need almost no input current to control the load current.
- Motor switch FETs come in two different types: enhancement mode and depletion mode.
- If you put power on the gate of an enhancement-mode MOSFET, it makes the current flow faster.
- In depletion mode transistors, the voltage at the gate makes the resistance go down.
Applications of FET
- The important applications of MOSFETs are:
- To keep low intermodulation errors to a minimum, FETs (field effects transistors) are used in mixing circuits.
- FETs are used in low-frequency amplifiers since their connection capacitors aren't very big.
- You can change the voltage of a FET, which is why it is used in operational amplifiers as variable voltage resistors.
- Because they have a high input impedance, FETs are often used as input amplifiers in oscilloscopes, voltmeters, and other measuring tools.
- FET is also used to make radio frequency boosters for FM radios and TVs.
- FETs are used in TV and FM antennas to mix signals.
- FETs are also used in LSI (large-scale integration) and computer memory units because they are small.
What's Your Reaction?