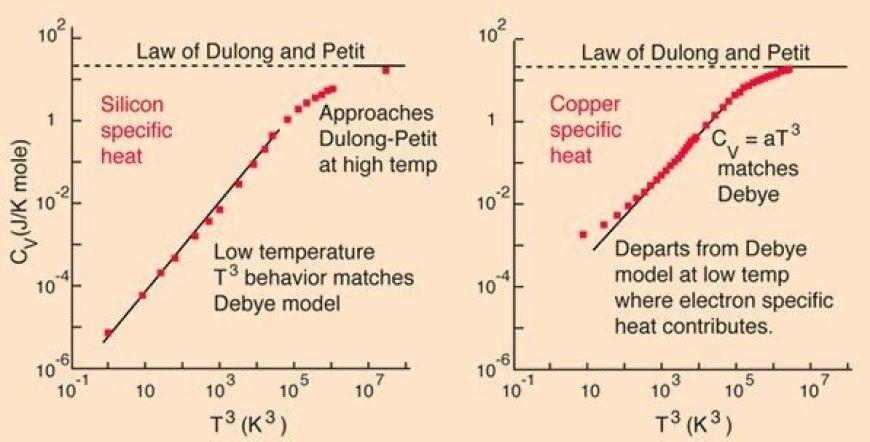
DULONG PETITS LAW
-Petit Law: Solid's heat capacity (roughly constant) reveals atomic weight secrets.
- There are three main types of matter: solid, liquid, and gaseous. You can change their physiological conditions by giving them the right temperature and pressure. That's also how you can change their balance points.
- Anything that wants to raise or lower its warmth needs energy from somewhere else.
- The temperature of gases doesn't change much when they are heated, but other things do change significantly. These things are volume and pressure.
- A substance's specific heat capacity is the amount of energy it takes to raise its temperature by one degree Celsius per unit mass.
Specific heat capacity of solids
- As matter types, solids have strong intermolecular forces, are hard, have the right shape and structure, and so on.
- You can heat things, which means you can find out how much specific heat they can hold. Certain heat capacities are measured in SI units, which are J/kg/K.
- A solid's specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise its temperature by 1°C for every unit mass of that solid.
- We will have to use the law of equal distribution of energy to find the specific heat capacity.
- According to this rule, there will be a certain amount of average energy for each degree of freedom a molecule has in a system that is thermally balanced.
- A gas atom moving in three-dimensional space, for instance, has three dimensions, so its degree of freedom would be 3.
- Take a look at any object that has N atoms. Every atom can move around easily, but only along one path or in one-dimensional space.
- The expression for the total energy U is given as: U = 3kbTNA = 3RT.
- For the first law of thermodynamics, we will use the following equation:
- ΔQ = ΔU+P ΔV
- There is only one way to change energy from one form to another, according to the first rule.
- This time, PV doesn't need to be used because the volume change for solids is so small.
- So, the formula for molar specific heat capacity (the amount of heat that can be stored in one mole of solid) is
As a general rule, C= Q/T= U/T.
C = 3R = 24.94 J/K-1 mol -1 C.
Here is the molar-specific heat capacity.
- T displays the change in temperature.
- Heat potential is pretty much a trait that is there by itself. This means it is a property of a certain material.
- Calorimeters are used to figure out the heat capacity. The volume readings on the bomb calorimeter are always the same.
- Coffee cup calorimeters are a different kind of calorimeter that can be used to find heat capacity at constant pressure.
What's Your Reaction?