CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
Continental Drift Theory: Once a giant landmass, continents drifted apart over millions of years.
CONTINENTAL DRIFT
- Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist, arctic explorer, astronomer, and geologist, proposed the Continental Drift Theory. He is frequently known as the "Father of Continental Drift."
- Wegener suggested the stunning hypothesis of 'continental drift' in a presentation in 1912.
- Continental drift refers to the movement of continents over the ocean bed.
- This drifting process takes millions of years to complete.
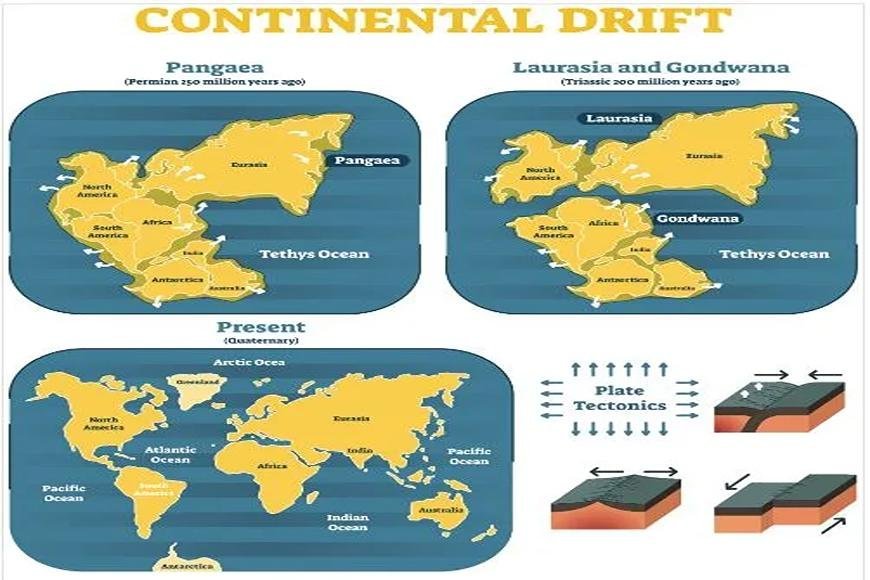
- According to Wegener, all of the continents combined to form a single continental mass known as "Pangaea," which means "all of Earth.
- " This supercontinent was encircled by a massive ocean known as "Panthalassa," which means "all water.
- Laurasia and Gondwanaland then split into the several smaller continents that exist today.
- Thus, Wegener postulated that continents float and move continually on the earth's surface. His notion later became the foundation of modern plate-tectonic theory.
Various Stages of Continental Drift Theory
- The first stage occurred during the Carboniferous period, when Panthalassa, a mega-ocean, ringed Pangea, a supercontinent.
- Around 200 million years ago, during the Jurassic period, the supercontinent Pangaea began to divide.
- Pangaea originally split into massive continental masses known as Laurasia and Gondwanaland, with the northern and southern components being Laurasia and Gondwanaland, respectively.
- During the Mesozoic period, the Tethys Sea gradually occupied the territory between Laurasia and Gondwanaland, and it steadily enlarged.
- Around 100 million years ago, North and South America moved westward, culminating in the formation of the Atlantic Ocean.
- The westward movement of North and South America generated the Rockies and Andes.
- The fifth orogenetic stage, during which mountain-building activity occurred, is the orogenetic stage.
Criticism of the Theory of Continental Drift
- The hypothesis of continental drift was clearly compelling.
- However, much of the hypothesis was based on conjecture and insufficient data. It sparked a lot of criticism and debate.
- The contentious causes that were said to have produced the drift were the source of the most severe criticism of this theory.
- According to experts, if the moon's or sun's gravitational force was strong enough to cause the landmass to break, it would have stopped the rotation of the earth and made it stationary.
- Also, in order to cause a drift in a landmass, the required rotations should be at such a high speed that they would have thrown the atmosphere (the gases) and everything else in outer space away from the earth's gravitational pull.
- There is no evidence of precarboniferous history.
What's Your Reaction?