SEISMIC WAVES
. Seismic waves - P and S waves - travel through our planet, revealing its secrets.
-
Earthquakes are transported by waves that flow through the earth, essentially using it as a medium to convey massive quantities of energy. These are known as seismic waves.
Types of seismic waves
- The Earth's crust is a solid rock that sits directly underneath the continents and seas.
- The crust is divided into plates that can sometimes move against each other, causing significant friction.
- This friction can cause vibrations (disturbances) in the crust, which cause seismic waves.
- Seismometers are pieces of equipment that may be used to measure earthquake magnitudes by creating a seismogram that can be read to determine the amplitude and intensity of the associated seismic waves.
- These seismic waves are classified into two types: body waves and surface waves.
- Body waves are seismic waves that move into the Earth's core layers, whereas surface waves only travel over the Earth's surface.
- According to the definition of a seismic wave, surface and body waves both transmit energy through the Earth.
Types of seismic waves
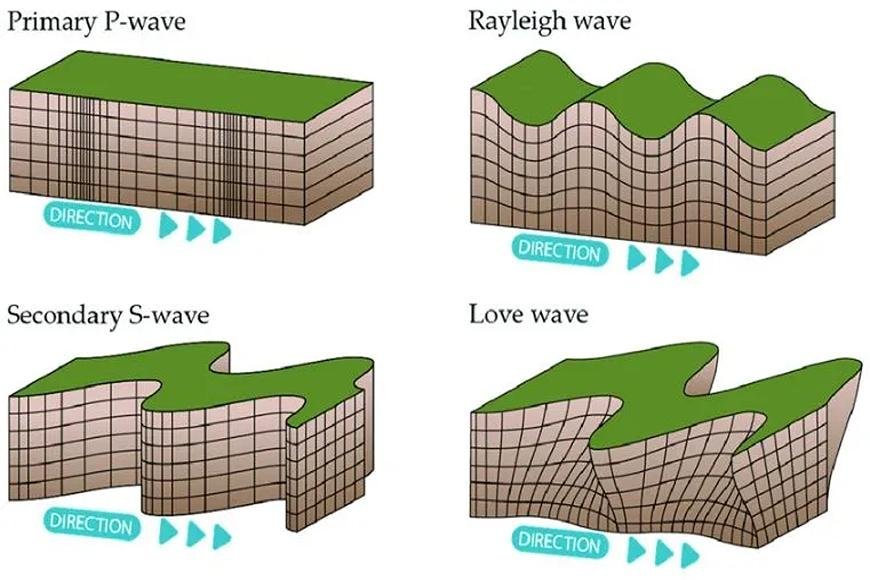
P-waves
- The first sort of seismic wave we shall investigate is the P-wave.
- When an earthquake happens, the first waves to be felt are generally P-waves or primary waves.
- This is because P-waves move the quickest of all earthquake waves.
- P-waves are body waves because they travel through the Earth's interior layers at speeds of around 1500 m/s in water and 5000 m/s in granite.
- P-waves may pass through the inner core, outer core, and mantle, as well as solid earth and water.
- P-waves are other examples of longitudinal waves.
- That is, the material of the medium through which a P-wave travels will vibrate in the same direction as the wave.
- Because P-waves have small amplitudes, their impacts on the ground are mild and often do not cause significant harm.
- P-waves force material to compress and expand as they pass through the medium due to their longitudinal character.
S-waves
- Secondary waves, often known as S-waves, are seismic waves that move at roughly half the speed of the main waves.
- As a result, their impacts are felt only after the effects of the P-waves during an earthquake.
- S-waves are categorized as body waves since they flow through the Earth's interior layers.
- S-waves cannot travel through water, but only through solid material, and hence only through the mantle.
- Transverse waves are S-waves. This indicates that the medium's substance travels from side to side while the wave moves perpendicular to the material's motion.
- S-waves have a larger amplitude than P-waves; hence, their impacts are more severe and can cause more harm.
- S-waves induce shear in the medium of propagation's substance.
Rayleigh waves
- Rayleigh waves are seismic waves that travel at a speed that is 80% to 90% that of S-waves.
- These waves' impacts are generally felt immediately after the S-wave has gone.
- Combining transverse and longitudinal motion produces Rayleigh waves.
- The Earth's material flows in circular routes, whereas the wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to the plane of these circles.
- Because Rayleigh waves are categorized as surface waves, their impacts are far more harmful than those of primary and secondary waves.
- Because of the circular nature of surface material motion, the earth moves up and down as the Rayleigh wave moves.
- This implies that they convey all of their energy throughout the earth's surface, causing significant shaking and damage.
Love Waves
- Love waves are the last of the seismic waves.
- They travel at a slower rate than S- and P-waves but somewhat quicker than Rayleigh waves.
- Love waves are transverse, and the Earth's surface material travels perpendicular to the direction of wave motion, with an amplitude parallel to the surface.
- Love waves are surface waves, and their energy is instantly transferred to structures and things on the ground.
- Outside of the core of an earthquake, love waves can cause the most destruction and harm.
What's Your Reaction?