ARTICLES
Articles ("a/an/the") in English act like traffic signs, guiding readers if something is general (a/an) or specific (the).

ARTICLES
Within the intricate tapestry of English grammar, articles, often referred to as determiners, play a fundamental role in establishing definiteness and specificity, thus enhancing clarity and precision. This exploration delves into their functions and nuances, adhering to the formal register found in academic texts.
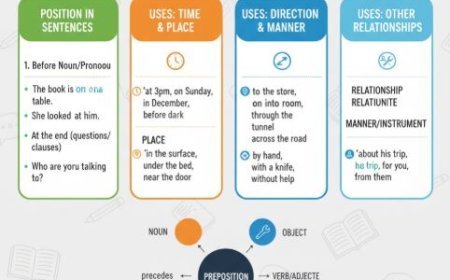
1. THE INDEFINITE ARTICLES: "A" AND "AN"
- These indefinite articles introduce novel and non-specific nouns, acting as linguistic pioneers venturing into the unknown.
- Imagine encountering a fascinating artifact in a museum, or delving into an unexplored linguistic phenomenon. They evoke a sense of discovery and possibility, marking the initial encounter with a new concept.
Examples:
- A hypothesis can pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries.
- An experiment can yield unexpected results, challenging established paradigms.
- A journey of linguistic exploration begins with a single word, opening doors to diverse worlds of meaning.
2. The Definite Articles: "The"
This definite article serves as a linguistic beacon, pointing to specific, previously mentioned, or unique nouns. Picture revisiting the artifact that captivated you at the museum, or cherishing the knowledge gained from your exploration of the unexplored linguistic phenomenon. It creates a sense of familiarity and recognition, grounding the reader in the established context.
Examples:
- The Mona Lisa, with its enigmatic smile, continues to captivate millions of viewers worldwide.
- The cosmos, enormous and ever-expanding, offers innumerable secrets yet to be solved.
- The key to effective communication lies in understanding the nuances of language, including the proper use of articles.
3. Beyond the Fundamentals
- Countable Considerations: Utilize "a/an" with countable nouns (one book, two books), and "the" with uncountable nouns (the water, the air).
- Exceptional Encounters: "The" can sometimes introduce new information with a sense of uniqueness (e.g., "The very idea!").
- Naked Nouns: Occasionally, nouns stand alone without articles, often conveying general ideas or truths (e.g., "Honesty is valued").
What's Your Reaction?