ESR Spectrometers and Hyperfine Structure
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) detects unpaired electrons using a microwave source and a magnetic field. The ESR spectrometer measures how these electrons absorb energy when transitioning between spin states. The total Hamiltonian describes the system’s energy, including electron–magnetic field interaction and hyperfine interaction. Hyperfine structure arises from coupling between electron spins and nearby nuclei, causing small energy-level splitting and offering detailed insight into local atomic environments.
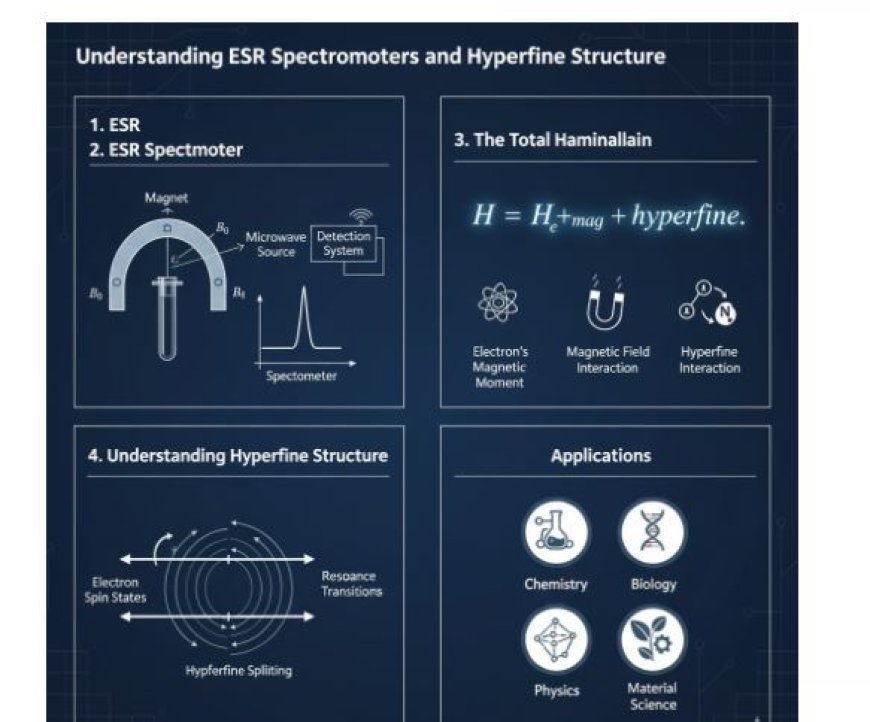
Understanding ESR Spectrometers and Hyperfine Structure
1. ESR
1.1 Definition
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) is a way to look at things with a spectrometer and find electrons that are not paired up. Some atoms and molecules have electrons that are not paired up with anything else. How these electrons behave in magnetic fields can tell you a lot about the features of the material.
1.2 Applications
ESR is used in many areas, such as:
- Chemistry: To learn more about free radicals.
- Biology: To look into biomolecules.
- Physics: To learn about solid-state materials and how magnets work.
2. Spectrometer for ESR
2.1 Basic Components
For electron spin resonance studies, the main tool that is used is an ESR analyser. Its most important parts are:
- Microwave Source: This makes microwaves that get the electrons moving.
- Magnet: Makes a magnetic field that lines up the electrons' spins.
- Detection System: Checks the signs that come after the electrons reverberate.
2.2 How It Works
- Alignment: An electron that is not paired with anything else can align with or against a magnetic field, making different energy levels.
- Microwave Excitation: Microwaves are used to move electrons from a state with less energy to one with more energy.
- Signal Detection: When the electrons return to their normal state, they give off energy that is picked up and saved.
3. The Total Hamiltonian
3.1 Hamiltonian
In quantum physics, the Hamiltonian is a mathematical function that shows how much kinetic and potential energy are in a system as a whole.
3.2 Components of the Total Hamiltonian in ESR
The Total Hamiltonian for ESR has terms that take into account:
- Electron's Magnetic Moment: Shown by its spin.
- Magnetic Field Interaction: Looks at how the electron spins interact with the magnetic field.
- Hyperfine Interaction: Describes how an unpaired electron interacts with nearby atomic nuclei.
3.3 Importance of the Total Hamiltonian
- Scientists can guess how the energy levels will split in a magnetic field by solving the Total Hamiltonian.
- This helps them figure out how the unbound electrons behave.
4. Understanding Hyperfine Structure
4.1 Definition
- Small changes and splits in the energy levels of electrons happen when they combine with close atomic nuclei. This is called hyperfine structure.
- The resonant frequencies seen in ESR tests change slightly because of this interaction.
4.2 Causes of Hyperfine Structure
The cause of hyperfine structure is:
- Magnetic Interactions: The electronic energy levels are changed by the magnetic fields that the nuclei make.
- Spatial Dependence: The strength of the contact depends on how far away and which way the nuclei are pointing in relation to the electron.
4.3 Importance in ESR Studies
Understanding hyperfine structure is important because:
- It tells us about the electric world around the unpaired electrons.
- It helps us figure out which atomic nuclei are connected to the unpaired electrons.
What's Your Reaction?