VOLTAGE FOLLOWER GAIN
The voltage follower circuit, also known as a unity gain amplifier or buffer amplifier, has a gain of exactly 1. This means the output voltage (Vout) is equal to the input voltage (Vin).
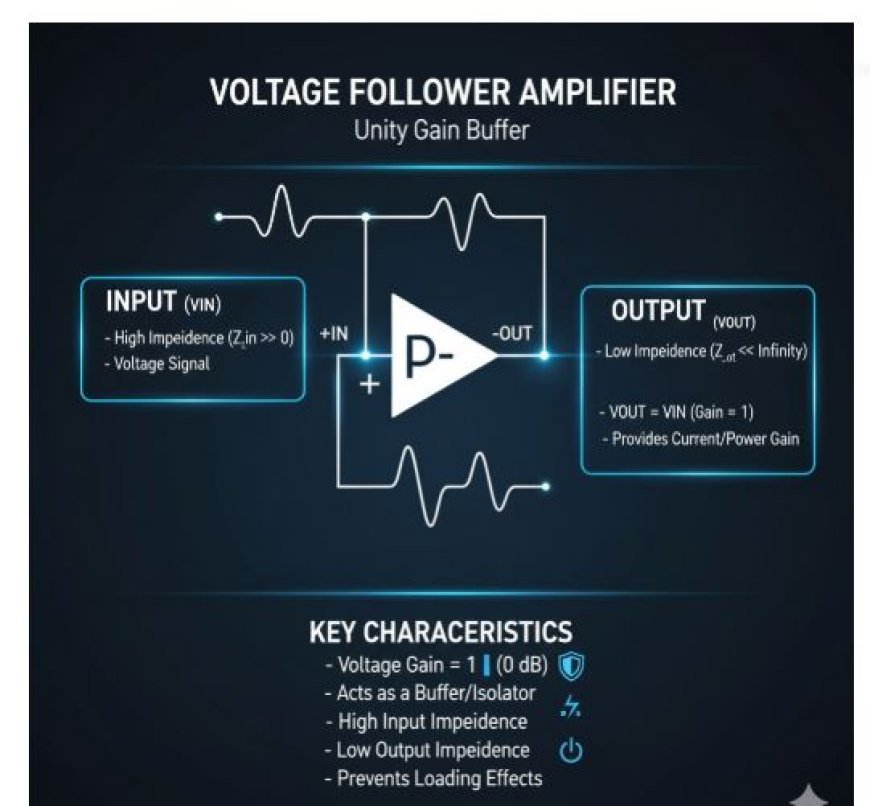
Voltage Follower
- A voltage follower is an op-amp circuit whose output voltage is equal to the input value (it "follows" the input voltage).
- As a result, a voltage-follower op-amp has a voltage gain of one and fails to improve the input signal.
- The voltage follower does not offer attenuation or amplification; it only serves as buffering.
- The input impedance of a voltage-follower circuit is quite high.
- Because of this property, it is a common option in a wide range of circuits that require isolation between the input and output signals.
Voltage Follower Gain
- Because the output voltage follows the input voltage, a voltage follower has a voltage gain of one (unity).
- Although a voltage buffer amplifier's voltage gain is close to unity, it gives significant current and power gain.
- Despite this, it is usual to refer to it as having a gain of 1—the voltage gain (the equivalent of 0 dB).
What's Your Reaction?