UNCONFIRMITY
An unconformity is a buried surface in rock layers that represents a gap in time between the formation of the rock units above and below it.
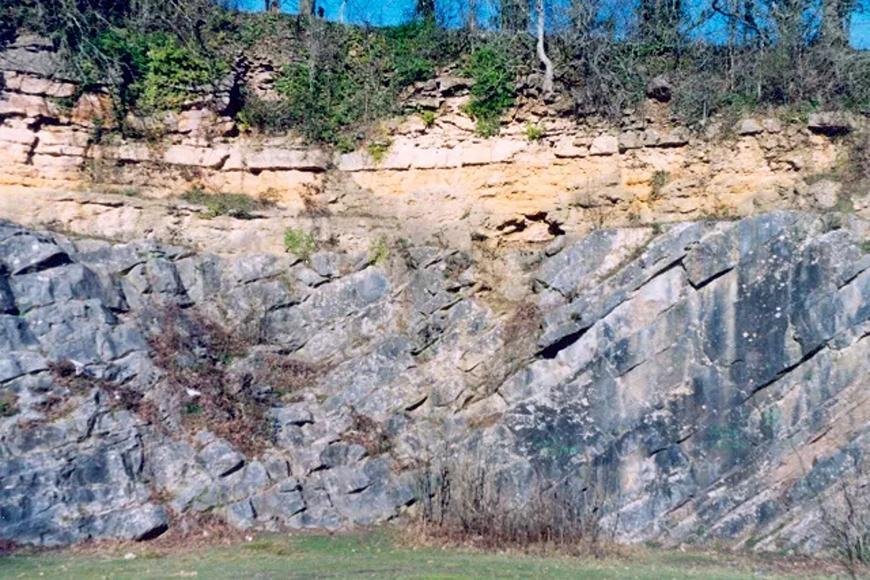

Unconformity
- A buried erosional or non-depositional surface that divides two different-age rock masses or strata indicates that sediment deposition was not continuous.
- Although the older layer was often exposed to erosion before the younger layer was evicted, the phrase is used to characterize any discontinuity in the sedimentary geological record.
Unconformity formation
- Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that can be used to identify events of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea-level changes.
- They are a feature of stratified rocks and are consequently most commonly found in sediments (but they may also be found in stratified volcanics).
- They are surfaces that produce a significant gap (hiatus) in the geological record between two rock masses (incorrectly, "time" is absent).
- Unconformities describe instances when deposition ceased, some previously deposited rock was removed by an erosion interval, and then deposition restarted.
Unconformity Types
Disconformity
- A disconformity is a gap between parallel strata of sedimentary rocks caused by erosion or non-deposition. Subaerial erosion characteristics distinguish disconformities.
- Soils and waterways from this type of weathering may be found in rocks.
- A paraconformity is a kind of disconformity in which the separation is only a bedding plane with no discernible buried erosional surface.
Nonconformity
- When the sedimentary rock rests above and was deposited on the pre-existing and eroded metamorphic or igneous rock, a nonconformity exists.
- The plane of junction is a nonconformity if the rock underneath the break is igneous or has lost its bedding owing to metamorphism.
Angular deviation
- An angular unconformity occurs when horizontally parallel sedimentary rock strata are deposited over tilted and eroded layers, causing angular discordance with the horizontal layers above.
- Later on, more orogenic activity may distort and skew the whole sequence.
Paraconformity
- A paraconformity is a kind of unconformity in which strata are parallel, there is no visible erosion, and the unconformity's surface resembles a simple bedding plane.
- Sometimes it's known as nondepositional unconformity or pseudoconformity. Diaastemas are short paraconformities.
- A diastem is a short paraconformity.
Buttress unconformity
- When younger bedding is placed against older strata, a buttress unconformity arises, altering the bedding structure.
Blended unconformity
- A blended unconformity is a type of disconformity or nonconformity that lacks a defined plane or contact separation and may consist of rock-derived soils, paleosols, or pebble beds.
What's Your Reaction?