PRONOUNS
Pronouns are short words like "she," "it," "you," or "we" that take the place of nouns.
PRONOUNS
Pronouns are special words that take the place of nouns we've already mentioned. They're like shortcuts that keep your writing clear and efficient.
Types of Pronouns
- Think of pronouns as different actors in a play, each with their own role:
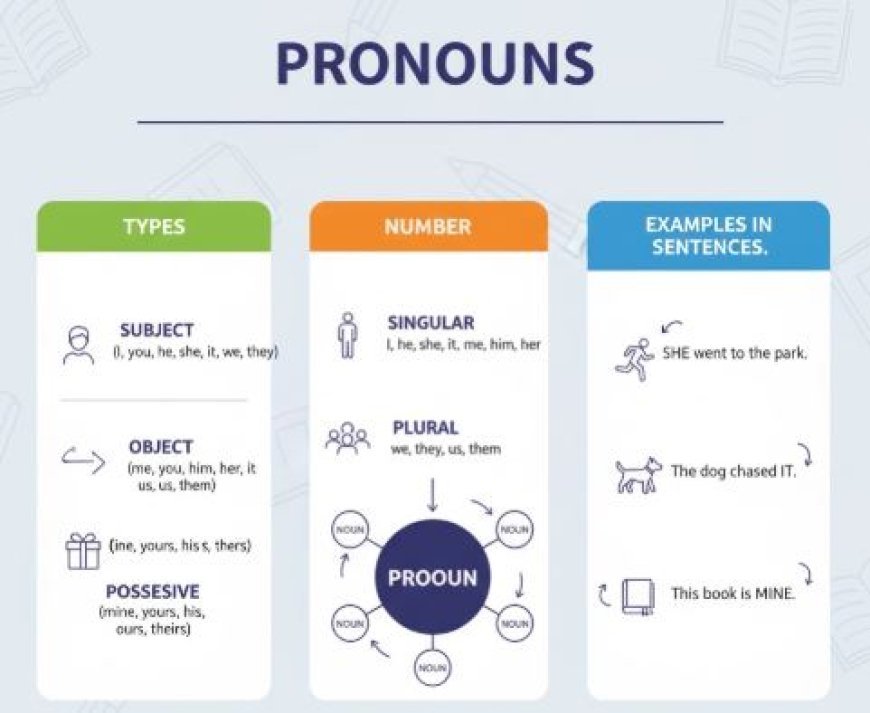
- Personal Pronouns: Refer to specific people or things:
Subject: I, you, he, she, it, we, they (e.g., Sarah went to the store, and she bought groceries.)
Object: Me, you, him, her, it, us, them (e.g., The teacher praised her for her excellent work.)
Possessive: Mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs (e.g., They finished their project and presented it proudly.)
- Reflexive Pronouns: Refer back to the subject, emphasizing the action:
Myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves (e.g., The artist painted herself in the mirror.)
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Point to specific things:
This, that, these, those (e.g., I prefer this book, but those look interesting too.)
- Interrogative Pronouns: Ask questions:
Who, what, which, whose (e.g., Whose phone is ringing?)
- Indefinite Pronouns: Refer to non-specific people or things:
Someone, something, nobody, anything, everyone, everything (e.g., Someone left the door open.)
Examples
- Possessive: The dog wagged its tail.
- Reflexive: She pinched herself to wake up.
- Intensive: I myself will handle this issue.
- Demonstrative: These are the best cookies ever!
- Interrogative: What is your favorite color?
- Indefinite: Several students were absent.
What's Your Reaction?