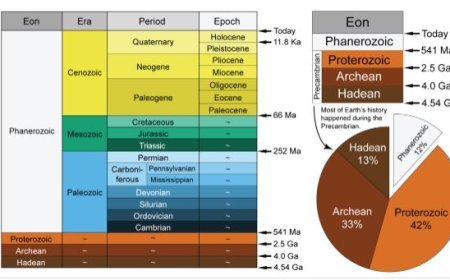
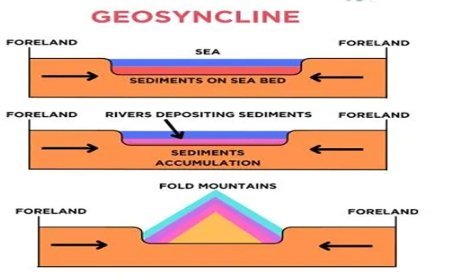
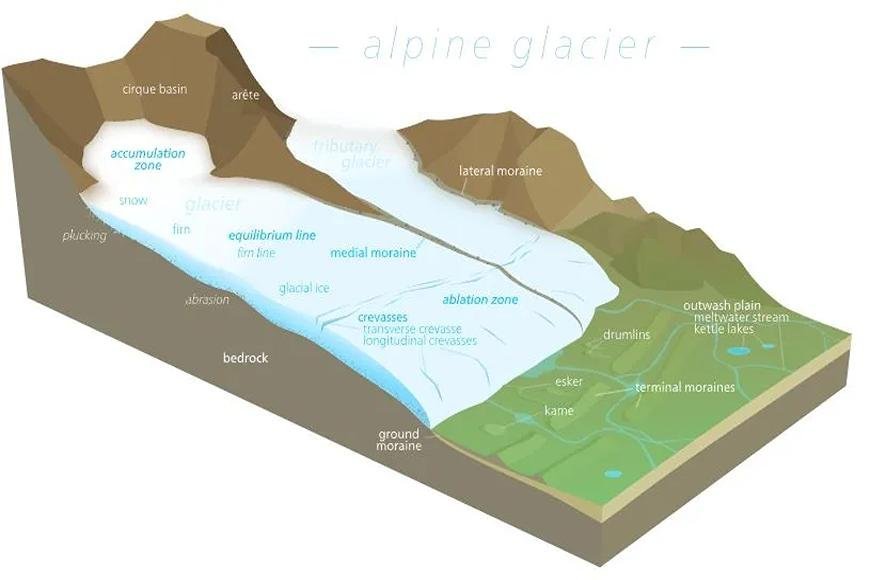
NATURE SCOPE AND COCEPT OF GEOMORPHOLOGY
From Plate Tectonics to Rivers: Geology & Geomorphology explore the forces shaping Earth's surface, past and present.
- The word "geomorphology" comes from the Greek words "geo," which means "Earth," "morph," which means "shape," and "logos," which means "thesis."
- It is the scientific study of the shapes and areas of land.
- The various climates on Earth are what create different types of landscapes. Mountains are not the same as deserts when it comes to shapes.
- The geomorphologist looks at these landscapes and studies their different parts.
- It tells us about how different shapes and forms in landscapes came to be.
The scope and nature of studying geomorphology
Nature
- Every day, the Earth changes, and these changes have a big effect on the living things that live on Earth.
- Geomorphology is the study of how different actions change the shape of the land.
- It helps us figure out what the land is like.
- The different geomorphic processes are looked at.
- The idea is about how landscapes are put together, how they change over time, and how they evolved.
- The skeleton is a group of parts that work together.
- Plate tectonics and volcano activity are among the factors that determine it.
- The geomorphic agents move with the help of water, wind, and other forces, lifting transports and placing earth materials.
- In the same way, Earth moves because of differences in pressure between areas with high pressure and areas with low pressure.
- When there are hills, the elements of nature become mobile; they move the materials away, push them over slopes, and store them at lower levels.
- Things like endogenic or exogenic forces are what cause the majority of processes. This process helps to shape the land.
The geomorphic process is split into two parts
- The Earth’s surface continuously undergoes internal and external forces.
- In addition, the internal forces are called endogenic forces, and the outward forces are called exogenic forces.
Endogenic forces
- The earth's primordial heat, earthquakes, rotational and tidal frictions, and radioactivity all contribute to the creation of endogenic forces.
Exogenic forces
- External forces, such as wind, moving water, groundwater, etc., come from the Earth's surface.
- Exogenic forces get their power from the atmosphere and help level out the Earth's surface.
- The exogenic process is also different in different places because of their climates.
Scope
- There are a lot of different ways to learn the idea of geomorphology, but there are three important ones:
- It is the investigation of the link between landforms and the underlying rocks
- It is the investigation of landforms and their evolution. Last but not least, the study of weathering is what makes landscapes possible.
- In this way, the idea of geomorphology includes the study of landscapes' processes, structures, and how they change over time.
- The structure is a list of all the parts of a system or physical thing that work together. It determines the study of geomaterials, such as how rock beds form and what rocks are made of.
- This process is related to the denudational process, which is another name for the outside forces that shape the surface.
- The study and development of landscapes over time involve how the surface interacts with things and how long the process lasts.
What's Your Reaction?