MODAL AUXILIARY
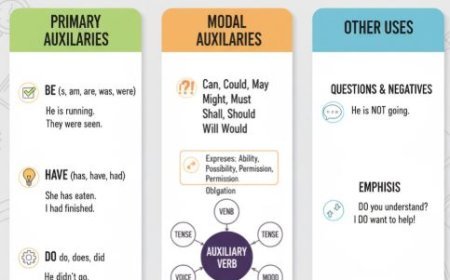
Modal auxiliary verbs in English are special helper verbs (like can, must, will) that you use with other verbs.
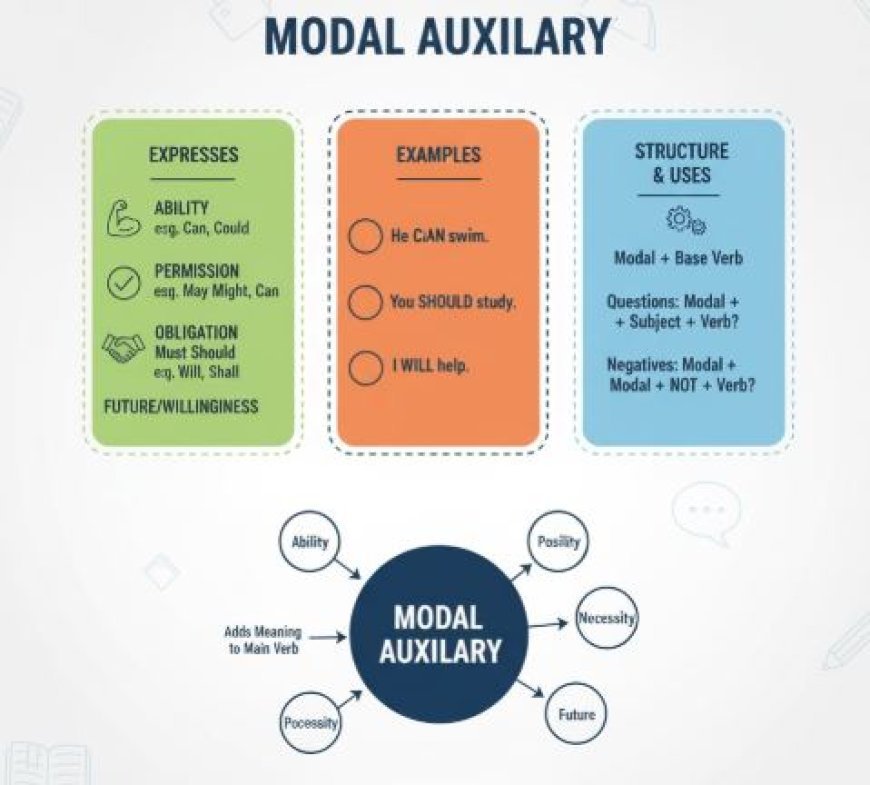
Introduction: Modal auxiliary verbs, often called modals, are special helpers in English grammar that add nuances to the meaning of a sentence.
Exploring Modal Auxiliary Verbs: Modal auxiliary verbs are like magic words that add special meanings to sentences. Here's a breakdown of their functions:
1. Expressing Possibility
- Modal auxiliary verbs like "can," "could," "may," and "might" express the idea of possibility. For example, "You can swim" denotes that you are capable of swimming.
2. Indicating Permission
- Modals such as "may," "might," and "can" can also indicate permission. For instance, "You may leave early" means you are allowed to leave early.
3. Giving Advice:
- Modal auxiliary verbs like "should," "ought to," and "had better" are used to give advice or recommendations. For example, "You should study for the test" suggests it's a good idea to study.
4. Expressing Obligation
- Modals like "must," "have to," and "need to" indicate duty or need. For instance, "You must finish your homework" means it's necessary to finish homework.
5. Showing Ability
- Modal auxiliary verbs like "can," "could," and "be able to" express ability or capability. For example, "She can speak Spanish" means she has the ability to speak Spanish.
6. Expressing Certainty
- Modal auxiliary verbs such as "must" and "will" express certainty or strong possibility. For instance, "It must be raining" suggests a high level of certainty about the weather.
What's Your Reaction?