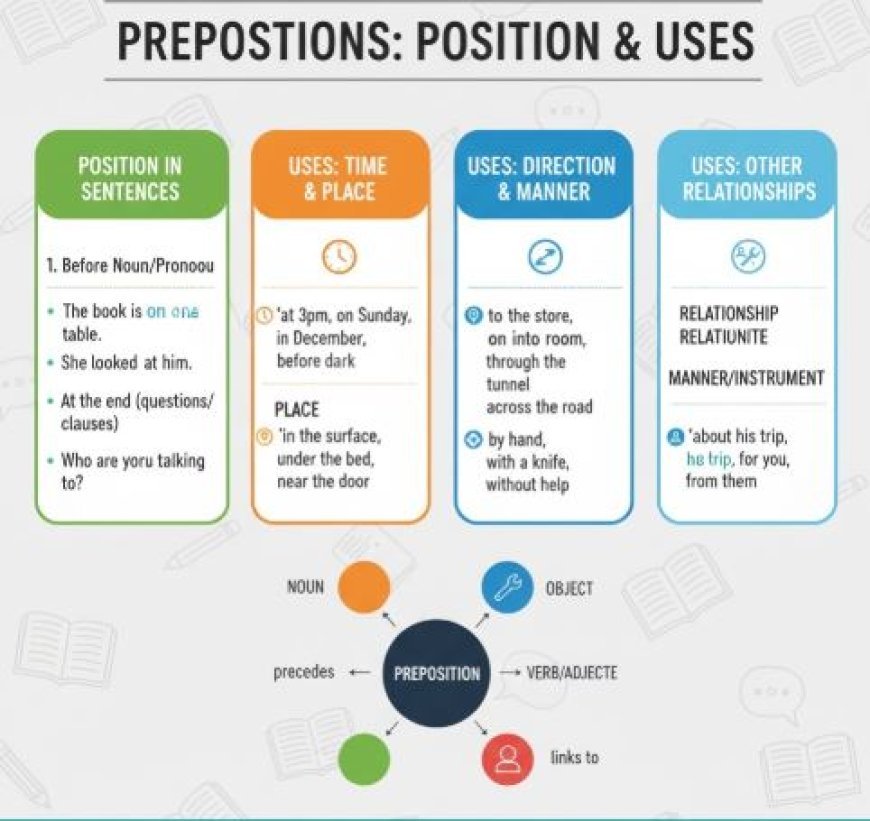
POSITION AND USES OF PREPOSITIONS
Prepositions: Grammar ninjas! They sneak in before nouns or pronouns, showing relationships like direction (to, from), time (before, after), or possession (of, with).
PREPOSITIONS
Prepositions are one of the most fundamental parts of speech in the English language. They are small but mighty words that play a crucial role in every sentence. In simple terms, prepositions are the words that indicate the relationship between different parts of a sentence. They describe the position of a noun or pronoun in relation to something else.
For example, the statement 'The book is on the table' employs the preposition 'on' to indicate the book's position relative to the table.
Position of Prepositions
Prepositions are usually placed before the noun or pronoun they are referring to. However, they can also be placed at the end of a sentence in some cases, which is known as a prepositional phrase. It is essential to place prepositions correctly to avoid changing the meaning of the sentence. For example, 'I was sitting on the chair' implies that you were physically on top of the chair, while 'I was sitting in the chair' suggests that you were sitting in the hollow space of the chair.
Use of Prepositions
Prepositions are used to show different relationships, such as location, time, and direction. Let's take a closer look at the usage of some common prepositions:
1. Location: Prepositions like 'in,' 'on,' and 'at' show the location of something.
For example, 'The cat is sitting on the table' or 'There is a bird in the tree.'
2. Time: Prepositions such as 'before,' 'after,' and 'during' indicate time relationships.
For example, 'We had breakfast before going to school' or 'The movie starts at 8 pm.'
3. Direction: Prepositions like 'into,' 'out of,' and 'towards' show the direction of something.
For example, 'She went into the room' or 'He is walking towards the park.'
4. Cause and Effect: Prepositions such as 'because of' and 'due to' are used to show the cause and effect relationship.
For example, 'The flight was cancelled because of the storm' or 'He failed the test due to lack of preparation.'
Adjective + Preposition
Sometimes, adjectives are followed by prepositions to specify their meaning further.
For example, 'fond of,' 'interested in,' and 'afraid of.' Let's take a look at a few more examples:
1. She is afraid of flying.
2. He has an excellent guitar playing style.
3. Sarah is angry with John.
4. I am tired of waiting.
5. The dog is scared of thunderstorms.
Verbs + Preposition
Certain verbs are also followed by prepositions to show their relationship with the object of the sentence. Here are some examples:
1. They apologized for being late.
2. He insisted on having the front seat.
3. Tom is looking forward to the weekend.
4. She apologized to her teacher for missing the class.
5. They succeeded in passing the exam.
What's Your Reaction?