BIOSTRATIGRAPHY
Learn about biostratigraphy, the study of fossils in rock layers, and its significance in reconstructing Earth's geological past. Explore the principles and applications of this vital field.
Biostratigraphy
- Biostratigraphy, or the study of fossils to date and connect rock strata, is an important technique for understanding Earth's past.
- We can untangle the chronology of life's development and our planet's shifting settings by examining the distribution of fossils across the geological record.
Biostratigraphic principles
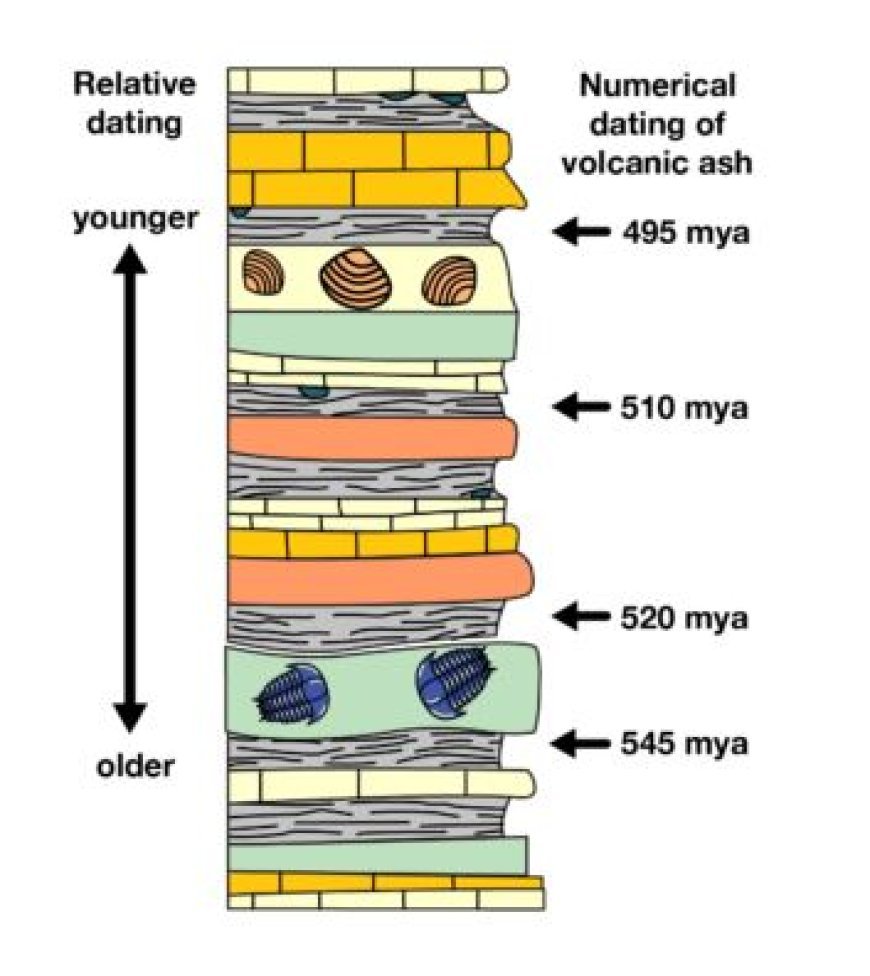
- Faunal Succession: Every geological epoch period has its own set of fossils. This notion is the basis for biostratigraphy, which allows us to identify and date rock strata based on their fossil richness.
- Index Fossils: Certain fossils, known as "index fossils," are useful for dating rocks because:
Wide Geographic Distribution: They are found across vast areas, making them important for connecting rocks from different locales. - Short Time Span: They evolved quickly, allowing for exact dating within a short span.
- Abundance: The species is well recognized and rather frequent, making identification easier.
- Biozones: The fossil record is classified into biozones, which indicate time periods characterized by the presence or lack of certain fossils.
- Range zones are determined by the earliest and final appearance of a given fossil species.
Concurrent range zones are defined by the overlap of the ranges of two or more species. - Assemblage Zone: A collection of fossils that are often indicative of a given habitat.
- Interval Zone: identified by the lack of a certain fossil.
Biostratigraphic subdivisions
1. Micropaleontology: Investigates minute fossils such as foraminifera and diatoms, which are plentiful and develop quickly, making them ideal for extensive biostratigraphic examination.
2. Palynology: the study of pollen and spores, which provides insights into previous vegetation and climatic change.
3. Vertebrate Paleontology: Investigates the fossil record of vertebrates, which helps us understand the evolution of numerous animal groups such as dinosaurs and mammals.
4. Invertebrate Paleontology: Investigates the fossil record of invertebrates like trilobites, ammonites, and brachiopods, which provides critical information for recreating former habitats and ecosystems.
5. Paleoanthropology: studies human evolution by examining fossils and artifacts to determine our species' lineage.
Applications of biostratigraphy
- Dating Rocks: Determine the age of rock formations and sedimentary sequences.
Correlation is the process of connecting rock units from different sites in order to uncover regional geological connections.
- Reconstruction of Past Environments: Investigating fossil assemblages to get insight into past ecosystems and climates.
- Petroleum exploration is the process of identifying prospective hydrocarbon sources based on the fossil content of rocks.
- Evolutionary studies involve tracing the history of life through the fossil record, which provides evidence for natural selection and adaptive change.
- Biostratigraphy is an effective instrument for revealing the mysteries of Earth's history.
- The fossil record reveals information on the history of life, historical environmental changes, and geological events that formed our world.
What's Your Reaction?