RING OF FIRE
Tectonic Fury: Plates Collide, the Ring of Fire Forms - Shaping Earth's Surface with Volcanoes and Earthquakes.
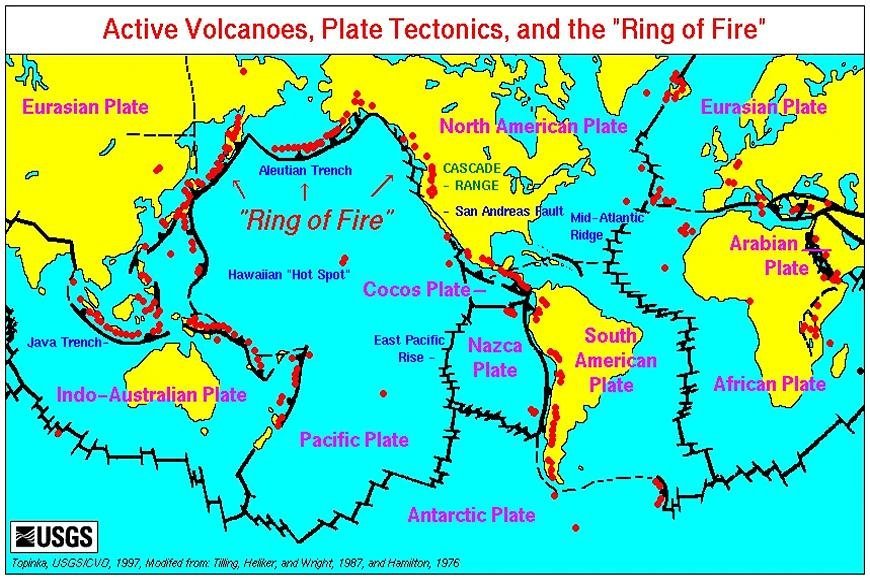
The Ring of Fire is the hottest place on Earth
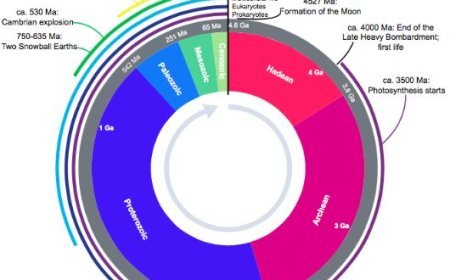
- The Ring of Fire, which is also called the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a zone of active volcanoes that forms a circle around the Pacific Ocean. It goes across a huge area, 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles), and includes many countries and regions. This hot spot isn't just an accident; it's a direct effect of how plate tectonics move and bend.
Here's a breakdown of the Ring of Fire's geology
Cause: There are subduction zones where oceanic plates, like the Pacific Plate, sink below the mainland or other oceanic plates. These zones are what cause the Ring of Fire. As the oceanic plate with more mass falls, friction and heat build up, which causes
Volcanism: Volcanoes like Mount Fuji and Mount St. Helens are made when molten rock rises from the ground.
Earthquakes: Tremors can be very strong or very weak, depending on how much friction and rock movement there is.
Key Features
Volcanoes
- Like Krakatoa, Kilauea, and Mauna Loa, the Ring of Fire is home to about 75% of the world's active and extinct volcanoes.
Earthquakes
- About 90% of the world's earthquakes happen in this area, and some of them are megathrust events that are stronger than 8.0 on the Richter scale.
Trench
- Deep ocean tunnels like the Mariana Trench mark the location where the subducted plate enters the mantle.
Island arcs
- Along the Ring of Fire, volcanic islands like the Aleutian Islands and the Japanese archipelago form as magma rises and cools.
What's Your Reaction?